样品实验方案
溶液配制
1.储备溶液配制
所有未使用的储备溶液应分为一次性使用的等分试样,并在制备后储存在-20°C下。 避免重复冻融循环。
链霉亲和素-Xtra 储备溶液(1 mg / mL):加入100 uL的Cat#46002和1 mL的Cat#46003的ddH2O,制成1mg/mL的储备溶液。注意:此重组溶液在4°C储存并避光保存后,可稳定保存6个月而无明显变化。为了更长的存储时间,可以将重构的溶液分成单次使用的等分试样,或者不分装添加等体积的甘油(最终浓度为50%),然后将溶液存储在-20°C(避光)。
2.工作溶液配制
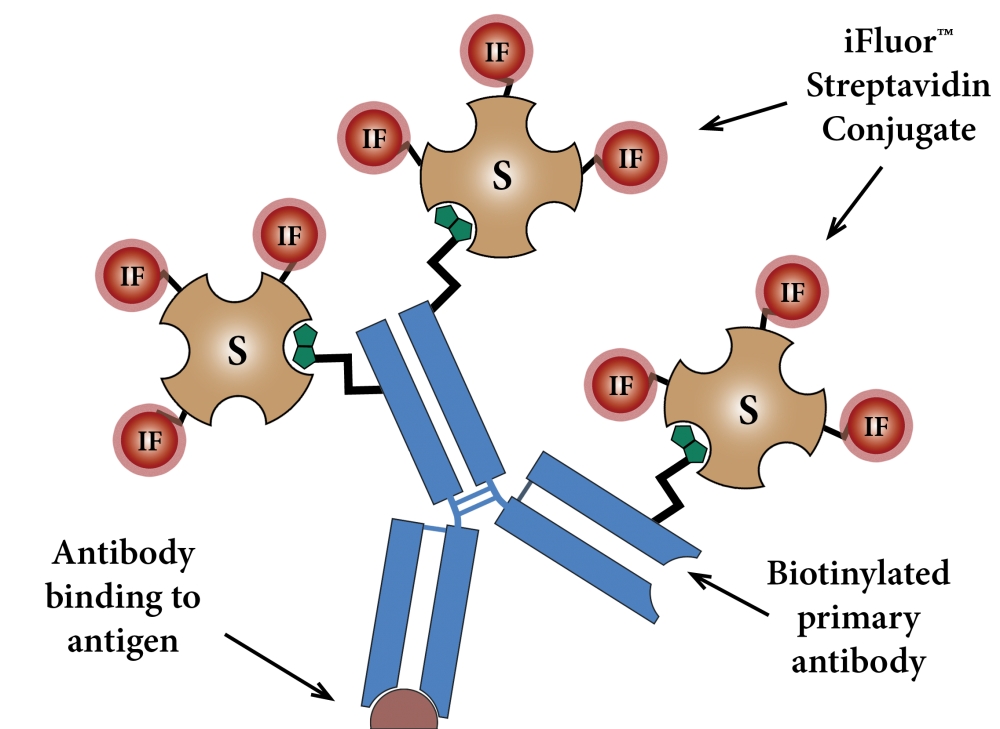
链霉亲和素-Xtra 工作溶液:对于IF,建议的染色浓度为1-5 ug / ml。对于FACS,建议在染色浓度为0.1-0.5 ug / 100 uL /百万细胞。注意: PBS + 0.1%BSA可用作染色缓冲液。 注意:为了获得每种应用的最佳性能,需要仔细确定该试剂的最佳浓度。注意: 建议的工作稀释度仅供参考,建议用户在测试中使用适当的阳性和阴性对照对产品进行滴定。
点击查看细胞制备方案
样品示例及操作
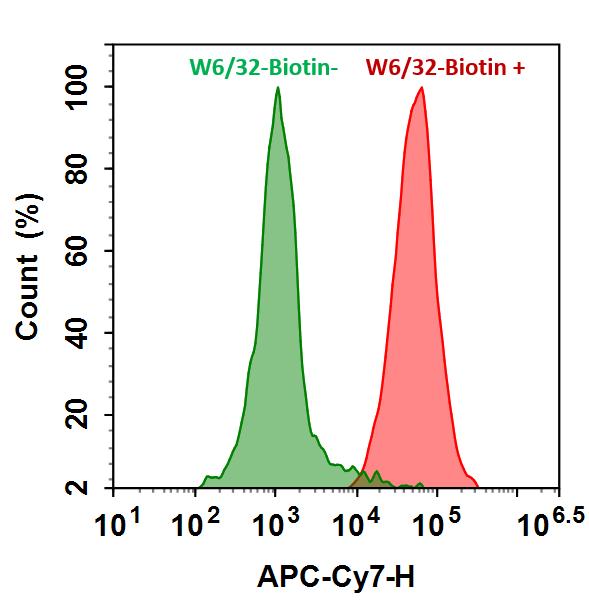
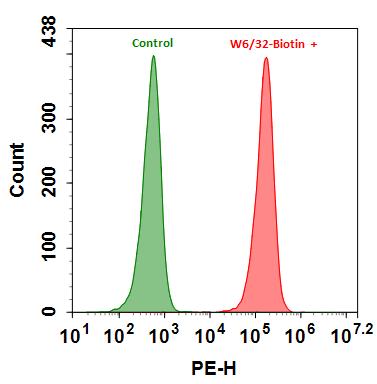
- 按照说明书中的建议用目标抗体封闭和处理样品。
- 在样品中以适当的浓度和持续时间添加生物素偶联的二抗工作溶液。注意:请验证您的生物素偶联抗体与实验中使用的一抗的相容性和类型。例如,如果一抗是小鼠抗体,则与生物素结合的山羊抗小鼠抗体可用于该测定。
- 在室温下用链霉亲和素-Xtra 工作溶液孵育细胞30分钟至1小时。 注意: 孵育的最佳时间需要仔细确定。
- 取出工作溶液,然后将细胞重悬在缓冲液中。
- 使用荧光显微镜拍摄图像或使用流式细胞仪记录强度。
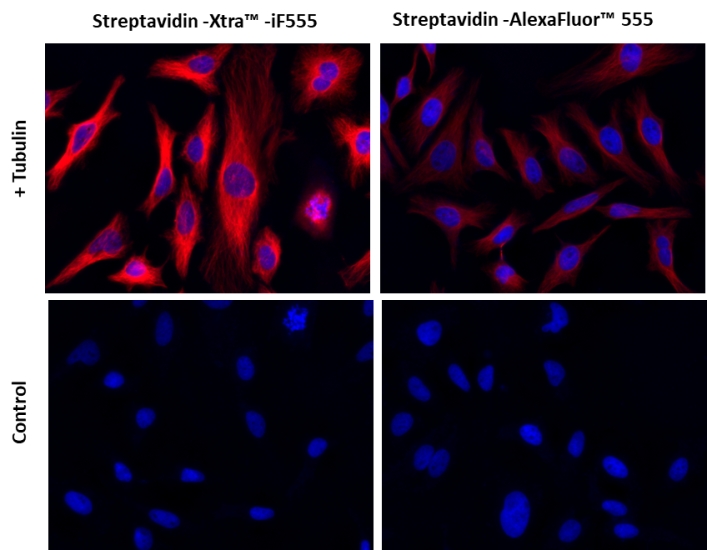
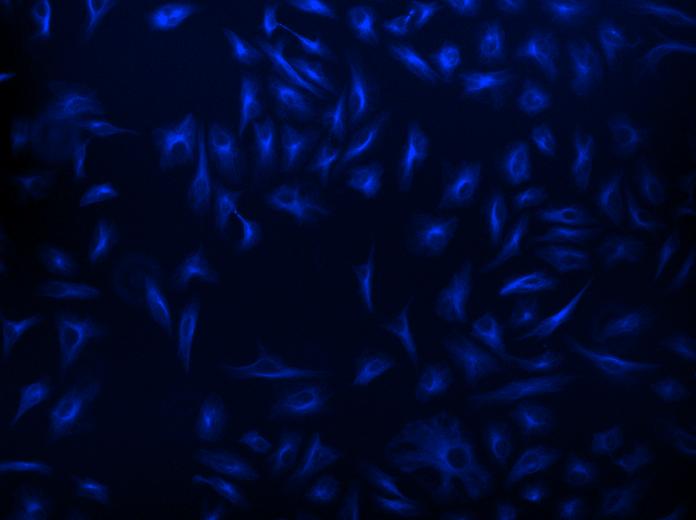
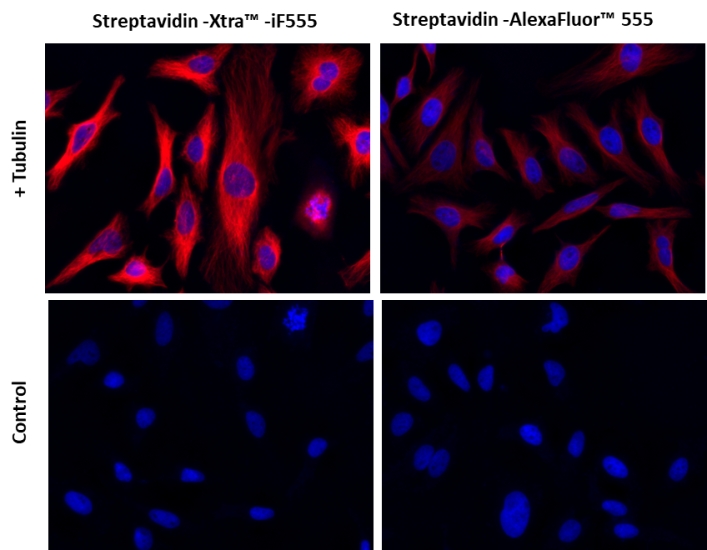
图1.用链霉亲和素-Xtra iFluor 缀合物和链霉亲和素Alexa Fluor 缀合物染色的Hela细胞图像。Hela细胞用4%多聚甲醛固定30分钟,用0.02%Triton X-100透化10分钟,并用1%BSA封闭1小时。然后将固定的Hela细胞在室温下用1 µg / mLα微管蛋白小鼠单克隆抗体染色1小时,然后用GxM IgG-生物素(货号16729)染色,然后用Streptavidin-Xtra iFluor 555和Streptavidin-Alexa Fluor 555染色。细胞核用Hoechst 33342(蓝色,货号17535)染色。
参考文献
Highly sensitive electrochemical biosensor for streptavidin detection based on CdSe quantum dots
Authors: Wei, Y. P., Liu, X. P., Mao, C. J., Niu, H. L., Song, J. M., Jin, B. K.
Journal: Biosens Bioelectron (2018): 99-103
Correction to Peptide Tag-Induced Horseradish Peroxidase-Mediated Preparation of a Streptavidin-Immobilized Redox-Sensitive Hydrogel
Authors: Mishina, M., Minamihata, K., Moriyama, K., Nagamune, T.
Journal: Biomacromolecules (2017): 311
Efficient streptavidin-functionalized nitrogen-doped graphene for the development of highly sensitive electrochemical immunosensor
Authors: Yang, Z., Lan, Q., Li, J., Wu, J., Tang, Y., Hu, X.
Journal: Biosens Bioelectron (2017): 312-318
High-sensitive surface plasmon resonance microRNA biosensor based on streptavidin functionalized gold nanorods-assisted signal amplification
Authors: Hao, K., He, Y., Lu, H., Pu, S., Zhang, Y., Dong, H., Zhang, X.
Journal: Anal Chim Acta (2017): 114-120
Biotin-Streptavidin Competition Mediates Sensitive Detection of Biomolecules in Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay
Authors: Lakshmipriya, T., Gopinath, S. C., Tang, T. H.
Journal: PLoS One (2016): e0151153
DNA-based hybridization chain reaction and biotin-streptavidin signal amplification for sensitive detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 through ELISA
Authors: Guo, Q., Han, J. J., Shan, S., Liu, D. F., Wu, S. S., Xiong, Y. H., Lai, W. H.
Journal: Biosens Bioelectron (2016): 990-995
Facile fabrication of an electrochemical aptasensor based on magnetic electrode by using streptavidin modified magnetic beads for sensitive and specific detection of Hg(2.)
Authors: Wu, D., Wang, Y., Zhang, Y., Ma, H., Pang, X., Hu, L., Du, B., Wei, Q.
Journal: Biosens Bioelectron (2016): 9-13
Highly Sensitive Two-Dimensional Paper Network Incorporating Biotin-Streptavidin for the Detection of Malaria
Authors: Grant, B. D., Smith, C. A., Karvonen, K., Richards-Kortum, R.
Journal: Anal Chem (2016): 2553-7
Increased electrocatalyzed performance through hairpin oligonucleotide aptamer-functionalized gold nanorods labels and graphene-streptavidin nanomatrix: Highly selective and sensitive electrochemical biosensor of carcinoembryonic antigen
Authors: Wen, W., Huang, J. Y., Bao, T., Zhou, J., Xia, H. X., Zhang, X. H., Wang, S. F., Zhao, Y. D.
Journal: Biosens Bioelectron (2016): 142-8
Peptide Tag-Induced Horseradish Peroxidase-Mediated Preparation of a Streptavidin-Immobilized Redox-Sensitive Hydrogel
Authors: Mishina, M., Minamihata, K., Moriyama, K., Nagamune, T.
Journal: Biomacromolecules (2016): 1978-84