上海金畔生物科技有限公司代理AAT Bioquest荧光染料全线产品,欢迎访问AAT Bioquest荧光染料官网了解更多信息。
Portelite 荧光总核酸定量试剂盒 *针对 Cytocite 和 Qubit 荧光计进行了优化*
| 货号 | 17631 | 存储条件 | Multiple |
| 规格 | 200 Tests | 价格 | 3612 |
| Ex (nm) | 509 | Em (nm) | 529 |
| 分子量 | 溶剂 | ||
| 产品详细介绍 | |||
简要概述
Portelite 荧光总核酸定量试剂盒用于快速测量核酸总量,包括样品中的双链 DNA (dsDNA)、单链 DNA (ssDNA) 和 RNA。 该试剂盒包含所有基本试剂,包括 Helixyte Green ssDNA 试剂、稀释缓冲液和预稀释的 DNA 标准品。 Helixyte Green All 试剂是一种灵敏的荧光核酸探针,用于测量样品中可能含有双链 DNA (dsDNA)、单链 DNA (ssDNA)、RNA 和长寡核苷酸的核酸总量。 Helixyte Green All 试剂不加选择地与 dsDNA、ssDNA 和 RNA 结合。 Portelite 荧光总核酸定量试剂盒针对使用 CytoCite 或 Qubit® 荧光计测量核酸总量进行了优化。
适用仪器
| 荧光定量仪 | |
| 激发: | 480nm |
| 发射: | 530nm |
| 材料: | 0.2 毫升 PCR 管 |
| CytoCite 荧光计 | |
| 激发: | 480nm |
| 发射: | 530nm |
| 材料: | 0.2 毫升 PCR 管 |
产品说明书
实验方案
概述
1.准备 Helixyte Green All 工作溶液
2.在每个 0.2 mL PCR 管中加入 190 µL 1X Helixyte Green All 工作溶液
3.在每管中加入 10 µL 核酸标准品或测试样品
4.在室温下孵育 2 分钟
5.使用 CytoCite 荧光计或 Qubit 荧光计检测荧光强度
溶液制备
Helixyte Green ALL工作溶液
1.用检测缓冲液(组分 B)将 Helixyte Green All 试剂(组分 A)稀释 200 倍。 例如,要为 5 个样品制备足够的工作溶液,将 5 μL Helixyte Green All(组分 A)添加到 1 mL 检测缓冲液(组分 B)中。
注意:通过用箔纸覆盖或将其置于黑暗中来保护工作溶液免受光照。 建议在塑料容器而不是玻璃容器中制备溶液,因为染料可能会吸附到玻璃表面。 为获得最佳效果,该溶液应在稀释后几小时内使用。
操作步骤
样品体积的可接受范围是 1~20 μL,具体取决于核酸样品的估计浓度。
以下方案是基于 10 μL 的样品体积生成的。
1.将 190 µL 1X Helixyte Green All 工作溶液添加到每个 Cytocite 样品管 (#CCT100) 或等效的 0.2 mL PCR 管中。
注意 使用薄壁、聚丙烯、透明的 0.2 mL PCR 管,例如 AAT Cat#CCT100。
2.每管加入10 μL核酸标准品或测试样品,涡旋2~3秒混匀。
3.在室温下孵育所有管子 2 分钟。
4.将样品插入 CytoCite 或 Qubit 并使用绿色荧光通道检测荧光强度。
标准校准曲线的制作
对于 Portelite 检测,您可以选择使用核酸标准品制作校准曲线。 这是生成定制 DNA 标准曲线的简要方案。
1.进行 1:2 连续稀释:将 10 ng/μL 核酸标准品 #2(组分 D)添加到检测缓冲液(组分 B)中以获得 10、5、2.5、1.25、0.62、0.31、0.15 ng/μL DNA 标准品 稀释。
2.将 190 µL Helixyte Green All 工作溶液加入每个管中。
3.将 10 µL 标准品加入 0.2 mL PCR 管中,然后涡旋混合 2~3 秒。
4.在室温下孵育反应 2 分钟。
5.将样品插入 CytoCite 并使用绿色荧光通道检测荧光强度。
图示
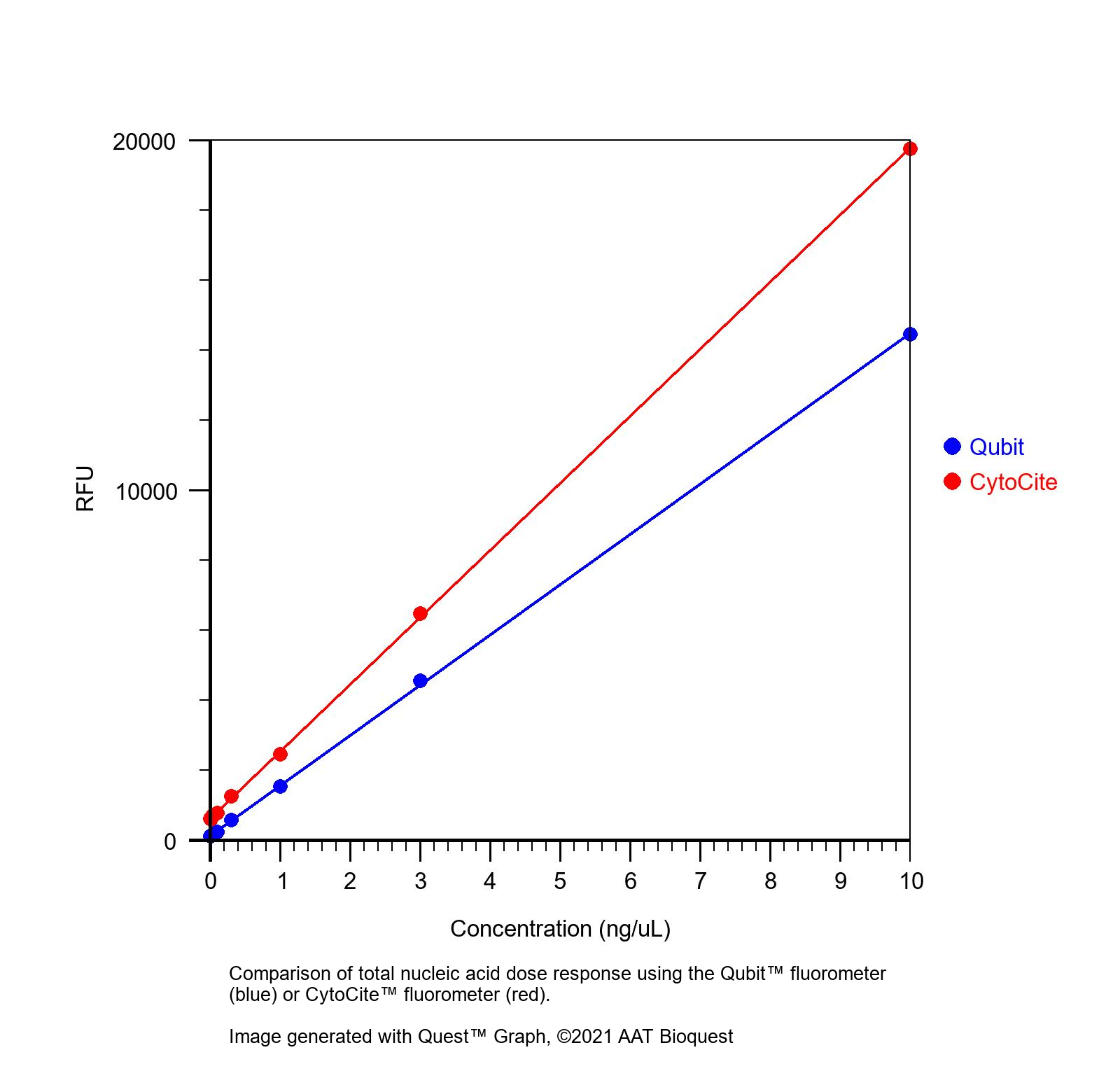
图 1. 使用 Qubit 荧光计(蓝色)或 CytoCite 荧光计(红色)比较总核酸剂量反应。
参考文献
Accurate bulk quantitation of droplet digital PCR.
Authors: Sun, Chen and Liu, Leqian and Vasudevan, Harish N and Chang, Kai-Chun and Abate, Adam R
Journal: bioRxiv : the preprint server for biology (2021)
Nucleic Acid Quantitation with Log-Linear Response Hybridization Probe Sets.
Authors: Wu, Lucia R and Fang, John Z and Khodakov, Dmitriy and Zhang, David Yu
Journal: ACS sensors (2020): 1604-1614
Nucleic Acid Extraction from Human Biological Samples.
Authors: Mullegama, Sureni V and Alberti, Michael O and Au, Cora and Li, Yan and Toy, Traci and Tomasian, Vanina and Xian, Rena R
Journal: Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.) (2019): 359-383
MICROFLUIDIC DEVICES FOR LABEL-FREE AND NON-INSTRUMENTED QUANTITATION OF UNAMPLIFIED NUCLEIC ACIDS BY FLOW DISTANCE MEASUREMENT.
Authors: Chatterjee, Debolina and Mansfield, Danielle S and Woolley, Adam T
Journal: Analytical methods : advancing methods and applications (2014): 8173-8179
Helicase-dependent amplification of nucleic acids.
Authors: Cao, Yun and Kim, Hyun-Jin and Li, Ying and Kong, Huimin and Lemieux, Bertrand
Journal: Current protocols in molecular biology (2013): 15.11.1-15.11.12
Concentration determination of nucleic acids and proteins using the micro-volume BioSpec-nano-spectrophotometer.
Authors: Sukumaran, Suja
Journal: Journal of visualized experiments : JoVE (2011)
Microvolume quantitation of nucleic acids.
Authors: Desjardins, Philippe R and Conklin, Deborah S
Journal: Current protocols in molecular biology (2011): 3J
Comparison of two real-time PCR methods for detection of ostreid herpesvirus 1 in the Pacific oyster Crassostrea gigas.
Authors: Martenot, C and Oden, E and Travaillé, E and Malas, J P and Houssin, M
Journal: Journal of virological methods (2010): 86-9
NanoDrop microvolume quantitation of nucleic acids.
Authors: Desjardins, Philippe and Conklin, Deborah
Journal: Journal of visualized experiments : JoVE (2010)
Effect of perinatal short-course zidovudine on the clinical and virological manifestations of HIV-1 subtype E infection in infants.
Authors: Sutthent, Ruengpung and Chokephaibulkit, Kulkanya and Piyasujabul, Daorung and Vanprapa, Nirun and Roogpisuthipong, Anuwat and Chaisilwatana, Pongsakdi
Journal: Journal of clinical virology : the official publication of the Pan American Society for Clinical Virology (2002): 47-56
